We are in a data-driven world then choosing the right database is really very important to manage your data and overall performance of an application. This article covers nine varieties of databases, what they are and how to use them with a few examples and describe some good database software you can use for each one.
1. Relational Databases
Relational database is to store data in tables (rows and columns) which relate to each other, it use Structured Query Language for querying. They preserve the integrity of data with table-to-table connections.
Use Cases
Transaction processing: Banking sector, Retail & Online transactions etc.
Banking Business use: CRM, ERP Systems
Data warehousing: Analytics and reporting
Example
For example, in a table representing customer data within a relational database you might have columns for CustomerID, Name, Email and PhoneNumber.
Popular Software
MySQL: Open source relational database.
PostgreSQL: The world’s most advanced open source database
Oracle Database: It Is an Enterprise Level Databases and Powered by Huge Arrays of Features.
Microsoft SQL Server: Comprehensive database solution for different applications.
2. Document Store Databases
Document stores, or Document-oriented databases store data as JSON, BSON or XML. It supports a flexible schema per document making it perfect for semi-structured or even unstructured data.
Use Cases
Content Management Systems: Websites, Blogging & CMS platforms.
E-commerce: Product catalogs
Real-time applications: Chat applications, Event logging
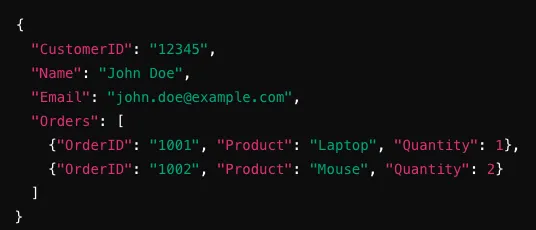
Example
As an example, a JSON document stored in some Document Store database can be represented like:
Popular Software
MongoDB: Popular document store database
CouchDB: Open Source document oriented DB
RethinkDB: Real-time database for the modern web
3. Key-Value Store Databases
Key-value stores are simple databases that maintain a collection of key-value pairs. These allow for quick access to data and can be scaled easily.
Use Cases
Caching: Saving most calls data
Session management: User sessions in a web application.
App Configuration Management: App Settings and Configuration
Example
A key-value pair in a Key-Value store would be:
Popular Software
Key: UserID_12345
Value: {"Name": "Ramesh Kum", "Email": "ramesh.k@example.com"}
Redis: NoSQL in-memory key-value store, super fast and puts almost no burden on your database.
Amazon DynamoDB: Key-value store fully managed by AWS
Riak: Is a highly-scalable, fault-tolerant distributed NoSQL key-value database
4. Columnar Databases
Columnar databases store information in columns not rows making this ideal for read-heavy operations or analytical query performance.
Use Cases
Data warehousing: Massive data analysis
Business intelligence: analytic and reporting
Real-time analytics: Realizing large dataset in real time
Example
Data for a table in the form of a columnar database may be stored as below
Column CustomerID: 12345, 67890, 23456
Column Name: John Doe, Jane Smith, Alice Johnson
Popular Software
Apache Cassandra: Most popular highly scalable columnar database
Google Bigtable: Google Cloud provides managed columnar database Service
HBase (Hadoop): An open-source, distributed database
5.Graph Databases
The data in graph databases is stored as nodes, edges and properties. They are designed to manage complex relationships and related data.
Use Cases
Social Networks: Monitoring and managing user associations & interactions.
Recommendation engines: What products/blogs to recommend
Detection of fraud: Detection of suspicious behavior patterns and links
Example
Example of a social network in which this might be represented by a graph database
Node: User with properties UserID, Name
Edge: FRIEND relationship between two User nodes
Popular Software
database.Neo4j: Leading graph database
AWS Neptune: A Fully-Managed Graph Database Service from Amazon
ArangoDB: The multi-model database with a lot of features for graphs DB.
6. Time-Series Databases
Time-series database are perfect for handling time-stamped data or time series data is going to get stored and queried efficiently. They are suited to high-write loads and time-range queries as well.
Use Cases
IoT Apps: Collection of data from sensors
Monitoring: Performance and system metrics
Pricing data: Stock prices, trading details and other financial market data
Example
Temperature sensor readings might be stored in such a way by a time-series database
Timestamp: 2023-07-06 12:00:00
Value: 22.5°C
Popular Software
InfluxDB: Time-series database written in Golang Open-source
TimescaleDB: Is an extension to PostgreSQL that provides time-series data functionality
Graphite: A monitoring tool which also happens to have time-series database
7. Object-Oriented Databases
Objects-oriented database: databases that store data as objects akin to object-oriented programming. They seamlessly integrate with OOP languages.
Use Cases
Complicated applications: CAD/CAM, software engineering
Real-time systems: Telecommunications and Embedded Systems.
Multimedia apps: Manage complex data structures
Example
An object in an object-oriented database might be a customer along with properties and methods.
Popular Software
ObjectDB: Object-Oriented Database for Java
db4o: Open source object DB
Versant Object Database: An object database focused on performance based applications
8. In-Memory Databases
Fast Read and Write: In-memory databases keep data in the RAM, where read and write operations are super-fast. They are great for high-output, low-latency applications.
Use Cases
A Real-time analytics: Processing and analyzing data, in real time
Rapid Data Access: Financial applications with frequency trading data
Example
A caching system using an in-memory database might store session data.
Key: SessionID_abc123
Value: {"UserID": "12345", "LoggedIn": true}
Popular Software
Redis: An in-memory data structure store with widespread adoption
Memcached: Distributed memory object caching system
SAP HANA: An in-memory relational database
9. Vector Databases
Many databases store data as high-dimensional vectors called a vector database. They are optimized for cases storing complex searches such as similarity search, recommendation systems.
Use Cases
Recommendation engines: Product/content recommendations
Image/video search: Buying similar photos or videos
Natural Language Processing: Text Similarity and Semantic Search
Example
The features of an image might be stored, in a vector database form:
ImageID: img_123
Vector: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, ...]
Popular Software
Pinecone: Handles similarity search using the latest scientific best-practices allowing for real time retrieval.
FAISS: Facebook AI similarity search library
Milvus: An Open-Source vector database for AI applications
You can achieve good data management and even better application performance by selecting right database.